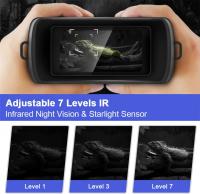
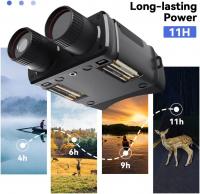
What Is Night Vision Goggles?
Night vision goggles (NVGs) are specialized optical devices designed to provide the ability to see in complete darkness or low-light conditions by detecting and amplifying ambient light, such as moonlight, starlight, or infrared light. These devices are widely used across a wide array of applications, from military operations and law enforcement to wildlife observation, search and rescue missions, and recreational activities such as hunting or exploring.
Although night vision goggles may seem like tools straight out of science fiction, they are based on sophisticated, well-researched technologies that have evolved significantly since their inception. This article aims to break down the mechanics behind night vision goggles, their different types, applications, and factors to consider if you're looking to purchase or use them.
---
How Night Vision Goggles Work: The Science Behind the Technology

Night vision goggles operate by amplifying very small amounts of available light and translating it into an image that is visible to the human eye. The technology primarily works through image intensification or thermal imaging.
1. Image Intensification:
The most common type of night vision technology amplifies ambient light, such as starlight or moonlight, which the naked eye struggles to detect. Here's how it works:
- Light Collection: The device collects light through the lens, including invisible infrared light.
- Photon to Electron Conversion: The incoming light particles (photons) hit a photocathode tube, which converts them into electrons.
- Amplification: These electrons are then accelerated using an electrical power source and passed through a microchannel plate (MCP), exponentially increasing their numbers.
- Creation of Image: The electrons strike a phosphor screen that converts the amplified electrons back into visible light, producing a bright, clear, green-tinted image.
The green hue is not accidental—human eyes can differentiate more shades of green than any other color, making it an ideal choice for night vision equipment.
2. Thermal Imaging:
Unlike image intensification, thermal imaging detects and visualizes heat (infrared radiation) emitted by objects, animals, or people. Objects emit different amounts of thermal radiation based on their temperature. Warmer objects appear brighter in thermal imagery, making it easier to detect them even in total darkness or environments where ambient light is unavailable.
---
Types of Night Vision Goggles

When choosing night vision goggles, it’s critical to understand their classifications and the generation (Gen) of technology they use. Each generation reflects improvements in performance, image quality, and functionality.
1. Generation 1 (Gen 1):
The earliest and most affordable form of night vision goggles. These devices rely heavily on ambient light, producing grainy, less-detailed images. Gen 1 devices are ideal for basic recreational activities but are not suitable for professional use.
2. Generation 2 (Gen 2):
A significant improvement over Gen 1 technology, these goggles include a microchannel plate that enhances light amplification. They perform better in darker environments and provide sharper images, making them suitable for law enforcement and security applications.
3. Generation 3 (Gen 3):
Gen 3 devices incorporate advanced gallium arsenide photocathodes and feature even better performance in low-light conditions. They are durable and provide high-resolution images, making them the standard choice for military forces worldwide.
4. Digital Night Vision:
A recent entrant into the market, digital night vision goggles convert light into an electronic signal, process it digitally, and display it on an LCD screen. While affordable, they consume more power and are bulkier compared to traditional analog systems.
5. Thermal Vision Goggles:
While not technically night vision goggles, thermal imaging devices are often used alongside or as an alternative to traditional night vision. They excel in situations where ambient light is entirely unavailable or obscured by environmental factors such as smoke or fog.
---
Applications of Night Vision Goggles

Night vision goggles are not just wartime aids—they have diverse applications across various industries and activities.
1. Military and Tactical Use:
The origins of night vision goggles are rooted in military use. Armies worldwide use them for night combat, reconnaissance missions, surveillance, and border patrols. Their ability to enhance situational awareness in low-light environments is irreplaceable during operations conducted at night.
2. Law Enforcement:
Police and security forces use night vision goggles for operations such as search and rescue, surveillance, and suspect apprehension, especially in poorly lit urban or rural areas.
3. Wildlife Observation and Hunting:
Biologists, researchers, and hunters rely on night vision goggles to study nocturnal animals or track game without startling them. This application is growing in popularity among nature enthusiasts looking to experience wildlife in its natural habitat after dark.
4. Search and Rescue Missions:
NGOs and emergency response teams use NVGs for locating missing persons after dark, particularly in dense forests, mountainous regions, or disaster-hit areas where visibility is low.
5. Recreational Use:
Enthusiasts and hobbyists involved in activities like camping, hiking, or nighttime photography increasingly incorporate night vision goggles. They help explore the world after sundown while maintaining safety.
---
Key Factors to Consider Before Buying Night Vision Goggles

Investing in night vision goggles can be overwhelming due to the wide variety of models and features available on the market. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
1. Purpose of Use:
Your intended use will guide your purchasing decision. Are you buying goggles for casual nighttime adventures, professional surveillance, or hunting? Recreational users may not need the high-end capabilities required by military personnel.
2. Generation:
As noted earlier, the technology generation determines image quality, light sensitivity, and durability. Generations 2 and 3 are generally recommended for professional use.
3. Field of View:
The field of view (FOV) denotes the width of the area visible through the goggles. A wider FOV allows better awareness of surroundings, which is crucial for tactical or search operations.
4. Weight and Comfort:
Since night vision goggles are typically worn for extended periods, their weight and ergonomic design play a critical role in user comfort.
5. Battery Life:
Night vision goggles rely on batteries for power. Devices with longer battery life or easily replaceable batteries are particularly important for extended use in remote areas.
6. Built-in Features:
Additional features such as water resistance, infrared illuminators, or a helmet-mounting option can enhance the usability of a device. Some models also offer dual-image fusion, combining thermal and image intensification capabilities for superior performance.
---
Limitations of Night Vision Goggles
Despite their advantages, night vision goggles do have limitations:
1. Dependence on Ambient Light:
Image intensification-based goggles require some ambient light to function; complete darkness can limit their effectiveness.
2. Incompatibility with Bright Light:
Exposure to sudden bright light can damage goggles and compromise image quality. Many advanced models come equipped with automatic brightness control to mitigate this issue.
3. Cost:
High-quality night vision goggles, particularly Gen 3 or thermal imaging models, can be prohibitively expensive for casual users.
4. Weather Sensitivity:
Performance may be hindered by rain, fog, or heavy snowfall, which can degrade visibility and intensification capabilities.
---
Conclusion: The Future of Night Vision
As night vision technology continues to advance, we can expect to see lighter, more durable, and more affordable models with superior clarity and innovative features. Augmented reality (AR) integration and artificial intelligence (AI) are future trends that may revolutionize this field by combining real-time information overlays with enhanced situational awareness.
Night vision goggles are no longer confined to military applications or professional fields—they are becoming increasingly accessible for everyday activities. Whether you're exploring the wilderness, keeping your property secure, or participating in tactical simulations, night vision goggles open up an unseen world of possibilities. However, choosing the right pair involves weighing your specific needs carefully against performance, durability, and cost.
By understanding the core principles behind how these remarkable devices work, their applications, and their limitations, you can ensure that you make a well-informed decision when investing in a pair of night vision goggles.