What Are Surveillance Cameras?
Surveillance cameras, commonly referred to as security cameras, are a category of electronic devices specifically designed to monitor areas and capture video footage for security and observation purposes. These devices play an integral role in modern security systems, both in public and private spaces, ensuring safety, monitoring activities, and deterring potential criminal behavior. With advancements in camera technology, the applications, capabilities, and significance of surveillance cameras continue to grow, shaping the way individuals, businesses, and governments approach security challenges.
The Concept and Evolution of Surveillance Cameras

Surveillance cameras originated as a simple means of monitoring areas visually and recording activities without manual observation. Their primary objective was to ensure that property and people were safeguarded against threats or to investigate events after they occurred. Over time, as technology progressed, surveillance cameras evolved from bulky apparatuses with limited capabilities to highly sophisticated devices boasting high-resolution visuals, night vision, remote accessibility, and even artificial intelligence (AI)-powered analytics.
In their earliest configurations, surveillance systems were analog, storing recordings on physical tapes and offering limited storage and image clarity. Eventually, analog systems paved the way for digital systems, which introduced higher quality recording, larger storage options, and advanced internet-based functionalities. Today, surveillance cameras operate in a variety of settings, from home security systems to large-scale city infrastructure designed for crime prevention.
Key Features of Modern Surveillance Cameras

Modern surveillance cameras have transcended their traditional role as passive filming devices and have adopted advanced features that meet rapidly changing security demands. Some of the distinguishing aspects include:
1. High-Resolution Imaging:
Modern surveillance cameras offer high-definition or even 4K video recording capabilities. This ensures clear image quality and detail, which is crucial for identifying faces, license plates, or other distinguishing features.
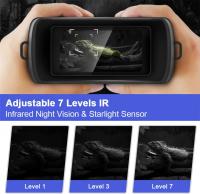
2. Night Vision and Infrared Capabilities:
Superior night vision ensures surveillance cameras remain effective even in complete darkness. Infrared lighting or low-light-enhancement technology equips these devices to capture clear images during nighttime or in environments with suboptimal illumination.
3. Remote Monitoring:
With internet-enabled surveillance cameras, users can access live footage and previously recorded videos remotely, whether through smartphones, tablets, or computers. This real-time access provides users with security updates anytime, anywhere.
4. AI Integration:
The incorporation of AI brings significant advancements to surveillance systems. Features such as facial recognition, motion detection, object tracking, and behavior analysis allow cameras to provide deeper insights, making them proactive rather than merely reactive.
5. Cloud Storage:
Cloud-based storage has addressed the limitations of traditional local storage solutions by enabling nearly unlimited data retention. Users can access recorded footage from centralized servers instead of relying on physical hard drives or SD cards.
6. Audio Integration:
Many modern surveillance cameras come with built-in microphones and speakers, enabling two-way communication. This feature is especially useful for scenarios like home security, where homeowners can communicate with visitors or delivery personnel directly through their cameras.
7. Durability:
Outdoor surveillance cameras often come equipped with weatherproofing and tamper-resistant materials to ensure they can withstand harsh environmental conditions and acts of vandalism.
Types of Surveillance Cameras

The versatility of surveillance cameras has led to the development of several models tailored to specific needs. Below is an overview of the main types:
1. Dome Cameras:
Known for their unobtrusive design, dome cameras are typically mounted on ceilings and offer a wide field of view. Their shape makes it harder to determine the direction they are pointing, adding an extra layer of deterrence.
2. Bullet Cameras:
Bullet cameras are long and cylindrical, making them ideal for outdoor use. They are often employed in situations requiring long-distance capture and can accommodate advanced zoom mechanics.
3. IP Cameras:
Internet Protocol (IP) cameras allow users to transmit video and receive analytics over the internet. They are perfect for homes and businesses that require remote monitoring or consistent internet-based updates.
4. PTZ Cameras (Pan-Tilt-Zoom):
Equipped with motorized lenses, PTZ cameras allow users to adjust the camera's field of view by panning, tilting, or zooming, making them particularly effective for monitoring large spaces.
5. Wireless Cameras:
Wireless cameras rely on Wi-Fi or other wireless protocols to transmit footage, thus avoiding the need for complex, hardwired installations. These cameras are popular for their ease of installation in residential settings.
6. Hidden Cameras:
Designed to remain discreet, hidden cameras are valuable for situations where inconspicuous surveillance is necessary. Examples include nanny cams or cameras integrated into everyday objects like clocks.
7. Thermal Cameras:
Using thermal imaging rather than visible light, these cameras detect heat signatures, making them ideal for perimeter security in low-light situations or areas with challenging environmental conditions.
Applications of Surveillance Cameras

The growing versatility and features of modern surveillance cameras have resulted in their deployment across diverse settings. Below are the most common applications:
1. Residential Security:
Homes are increasingly adopting surveillance cameras to monitor doorways, driveways, and interior spaces. Smart home security cameras can alert homeowners of unusual activity and provide peace of mind, even when they are away.
2. Commercial Security:
Businesses rely on surveillance cameras to protect their premises from theft, vandalism, and other security breaches. Retailers, for example, install cameras to minimize shoplifting and monitor daily operations.
3. Industrial Monitoring:
In industries like manufacturing or construction, surveillance cameras help ensure worker safety, monitor equipment usage, and prevent unauthorized access to restricted areas.
4. Public Safety:
Governments around the world use surveillance cameras to monitor streets, public buildings, parks, and transportation systems, making them an essential component of smart city security initiatives.
5. Healthcare:
Surveillance cameras in hospitals and clinics are used to monitor patient activity, secure sensitive areas, and observe staff interactions, ensuring patient care and safety.
6. Traffic Monitoring:
Surveillance cameras monitor roadways, helping regulate traffic flow and identify traffic violators or accidents in real-time. This data assists city planners in improving infrastructure.
7. Wildlife Observation:
In conservation and research efforts, cameras are set up to monitor wildlife populations without disturbing their natural habitats. These devices are also used to monitor poaching activities.
8. Event Security:
Events like concerts or sports games often use extensive camera systems to guarantee attendee safety and control crowd behavior.
The Benefits of Surveillance Cameras
There are numerous advantages to utilizing surveillance cameras, which make them indispensable tools for businesses, individuals, and authorities alike. These include:
- Crime Deterrence: The presence of visible surveillance cameras discourages trespassing, theft, and vandalism.
- Evidence Collection: Recorded footage serves as vital evidence in investigations, helping to resolve disputes or identify perpetrators.
- Cost Efficiency: Once installed, surveillance cameras are a cost-effective solution for long-term security monitoring.
- Remote Accessibility: Homeowners and businesses can check the security of their properties from hundreds of miles away using internet-connected devices.
- Operational Oversight: In addition to preventing crime, surveillance cameras enable employers to keep tabs on employee activities, ensuring productivity and adherence to company policies.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
While surveillance cameras bring numerous benefits, they also raise ethical and privacy-related questions. The advanced capabilities of modern cameras, such as facial recognition, may infringe on individuals' rights when used indiscriminately. For instance, in public spaces, consistent monitoring can lead to a perceived or actual invasion of privacy. In some cases, governments and organizations have faced backlash for their handling of surveillance data, particularly when such data is collected without adequate justification.
Balancing the necessity of security with privacy rights requires establishing clear regulations and fostering transparency. For individuals and businesses alike, understanding compliance requirements and implementing best practices becomes crucial in deploying surveillance systems responsibly.
Final Thoughts
Surveillance cameras are an indispensable asset in the modern world, providing safety, accountability, and operational enhancements across a variety of industries and environments. As technology continues to advance, their capabilities will only improve, offering even more sophisticated tools for fostering a secure and efficient society. However, the adoption of these technologies must involve careful consideration of ethical implications to strike a balance between protection and preserving individual freedoms.
Whether you’re planning to install a camera system for your home, your business, or your community, it’s vital to understand your specific security needs, be aware of the features available, and