How To Use Hidden Camera Detector?
In today’s digitally connected world, privacy is becoming an increasing concern. Advances in technology have made it much easier for hidden cameras to infiltrate private spaces without consent or even knowledge. Hidden cameras can potentially compromise personal security by invading homes, hotel rooms, meeting spaces, and more. With rising awareness of these risks, many individuals are now turning to hidden camera detectors to safeguard their environments. These devices help identify concealed cameras and provide peace of mind in uncertain settings. However, effectively using a hidden camera detector requires understanding how these devices work, their limitations, and the strategies for maximizing their performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into how to use hidden camera detectors appropriately. We’ll discuss the different types, typical situations where they are needed, step-by-step instructions for usage, and some additional hacks and best practices for ensuring optimal performance.
---
Understanding Hidden Camera Detectors
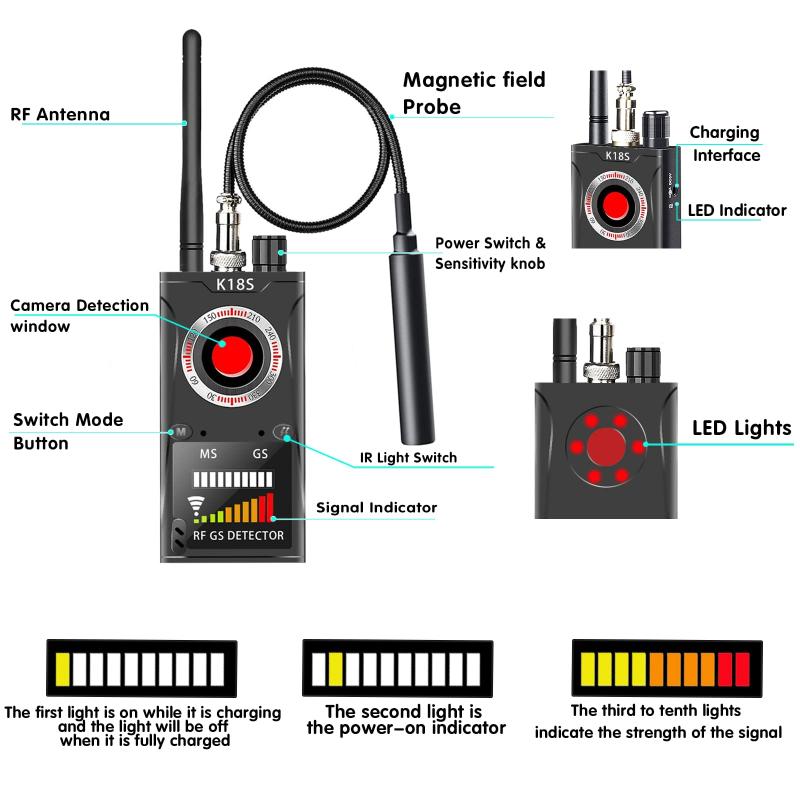
Hidden camera detectors are tools designed to locate surveillance devices that are hidden from plain view. They usually work based on two principles: detecting radio frequency (RF) signals or picking up on the reflective lens of a camera.
1. RF Signal Detectors: Many hidden cameras transmit video or audio wirelessly. RF detectors scan for electromagnetic signals being transmitted by these devices. Once a transmission signal is found, the detector can help you narrow down its location.
2. Camera Lens Finders: A more direct way to detect hidden cameras is by locating their lenses, which reflect light uniquely when illuminated with specific wavelengths. These types of detectors typically work by emitting infrared or red light and scanning for reflections indicative of camera lenses.
3. Hybrid Devices: These advanced detectors integrate both RF detection and lens finding methods, offering more comprehensive detection capabilities.
Each type of detector has its strengths and limitations. For instance, RF detectors work well for identifying actively transmitting devices but may not detect passive or non-operational cameras. Lens finders, on the other hand, can work on dormant cameras but require manual effort and a direct line of sight to the lens.
---
Common Scenarios Requiring Hidden Camera Detection

Hidden cameras have unfortunately been discovered in scenarios that should be safe and private. Here are some common situations where the use of camera detectors is especially essential:
- Public Accommodations: Hotels, Airbnb rentals, changing rooms, or public restrooms may sometimes harbor unauthorized hidden cameras.
- Workplaces: Detecting hidden monitoring in offices or meeting rooms can help protect sensitive information.
- Home Security Testing: Individuals concerned about invasions of privacy from landlords, neighbors, or others may wish to check their personal spaces.
- Travel: Rental vehicles or vacation properties can be checked to ensure they are free from unauthorized surveillance.
- Legal and Personal Disputes: Divorces, custody battles, or other conflicts may trigger covert surveillance concerns.
---
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Hidden Camera Detector

Efficient use of a hidden camera detector involves proper preparation, understanding typical hiding spots, and applying systematic techniques to ensure thorough detection. Below, we’ll outline how to use these devices effectively:
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Device
- Before using your detector, read the user manual thoroughly. Understand the key features, the type of detection it offers (RF, lens finder, or both), and how to operate it.
- Charge the device or ensure it has enough battery life for your inspection.
- If your device offers multiple scanning modes or sensitivity settings, familiarize yourself with how to toggle between them to fine-tune the search.
2. Prepare the Area for Inspection
- Switch off wireless devices (like phones, routers, and smart home gadgets) to reduce interference when using an RF detector.
- Reduce ambient lighting when using a lens finder to increase the visibility of any reflections.
- Identify and list the areas you wish to inspect. Surveillance devices are typically placed in places where they can capture the most activity, such as bedrooms, bathrooms, living rooms, or offices.
3. Search for RF Signals
- Turn on your RF detector and adjust its sensitivity. Begin scanning the room methodically, pausing whenever the device registers a signal.
- Move the detector slowly toward the source of the signal. The closer you get to the transmitting camera, the stronger the reading on the device.
- Inspect devices creating RF signals. While many household electronics such as Wi-Fi routers or smartphones emit legitimate wireless signals, devices in unexpected places (e.g., smoke detectors, clocks, wall outlets) warrant closer examination.
4. Use the Lens Finder
- Activate the optical scanning mode on your detector (if available). Look through the detector's viewfinder while shining its light around the room.
- Focus on areas where lenses are likely to be concealed. Common targets include light fixtures, air vents, mirrors, and small decorative objects.
- Look for a reflection – camera lenses typically produce a small, bright pinpoint of light when illuminated.
5. Inspect Common Hiding Spots
Hidden cameras are often strategically placed in locations that provide an unobstructed view of the area. Be sure to check:
- Electronic Devices: TV sets, DVD players, or speakers.
- Household Fixtures: Smoke detectors, thermostats, lights, or fans.
- Mirrors: Use the fingernail test. Place your fingernail on the surface of the mirror. If there’s a gap between the reflection and your nail, it’s a standard mirror. No gap could indicate two-way glass with a camera behind it.
- Unusual Objects: Decorative items like picture frames, alarm clocks, or even pens.
6. Cross-Check with a Physical Search
- Once your detector has helped you narrow down potential locations, physically inspect the suspect areas for hidden cameras.
- Look for small holes or unusual wiring that might house camera lenses or power components.
---
Additional Strategies and Tools for Enhanced Results

1. Smartphone Camera Test: In addition to specialized detectors, your smartphone can detect certain infrared lights emitted by hidden cameras. Point your phone’s camera at suspect areas in a dark room. If you see glimmers of light within your camera’s frame, further investigation is needed.
2. Use Professional Services if Needed: If you suspect a more sophisticated hidden surveillance system, or if you are unable to identify certain signals, consider hiring a professional bug sweeper or counter-surveillance expert.
---
Best Practices for Effectiveness
- Perform routine checks in sensitive spaces, particularly when traveling or staying in unfamiliar environments.
- Stay vigilant about device placement. Most surveillance requires a direct line of sight to the subject.
- Regularly update your detection equipment and make sure it’s compatible with the latest surveillance technologies.
---
Limits of Hidden Camera Detectors
While hidden camera detectors are excellent tools for safeguarding privacy, it’s important to recognize their limitations. For instance:
- RF detectors won’t detect cameras that are off or not transmitting.
- Lens finders can miss lenses that are obstructed or situated behind thick material.
- Small, pinhole cameras can be incredibly discreet, requiring patience and thoroughness to locate.
---
Closing Thoughts
In an era of heightened awareness about digital privacy and surveillance risks, hidden camera detectors provide a valuable line of defense in maintaining personal and professional security. With the right tools and proper techniques, you can effectively identify and neutralize potential threats to your privacy. The key is a combination of vigilance, systematic search methods, and the strategic use of technology.
Whether you’re concerned about covert surveillance in public accommodations or just want peace of mind in your personal space, proactive measures can make a significant difference. By understanding how these detectors work and leveraging them effectively, you can empower yourself to create safer, more secure environments wherever you go. Protecting your privacy isn’t just about technology – it’s about adopting a mindset that prioritizes awareness and security in every situation.