How Are Wireless Cameras Powered?
Wireless cameras have become increasingly popular due to their flexibility, ease of installation, and ability to provide security without tethering to cumbersome wires. A common question among potential users of wireless cameras is: "How are these devices powered?" Understanding the power options and infrastructure behind wireless cameras is crucial to making the best choice for your security needs. This article dives deep into this topic, explaining how wireless cameras are powered, exploring their power options, and offering practical tips to address common challenges.
The Basics of Wireless Camera Power
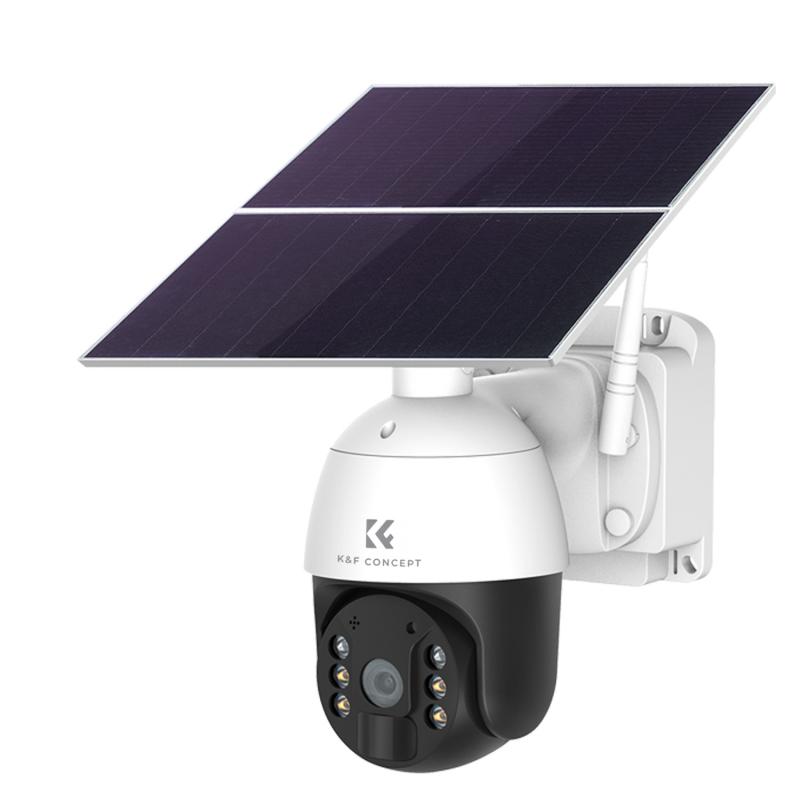

Wireless cameras offer the advantage of not being physically connected to a central monitoring station by data cables. However, they still require power to function, and this power can come from several sources. Wireless cameras are typically powered in one of two main ways:
1. Battery-Powered Wireless Cameras
2. Hardwired (Continuous Power) Wireless Cameras
Each of these methods has its own advantages and limitations, which we’ll explore in detail below.
1. Battery-Powered Wireless Cameras

Battery-powered wireless cameras are designed for maximum flexibility and portability. Since they don’t require a constant connection to a power outlet, these cameras allow you to install them in virtually any location, even in areas where electrical outlets are not available.
How They Work

Battery-powered cameras operate entirely on rechargeable or replaceable batteries. The camera often uses energy-efficient hardware and features, such as motion sensors, to conserve battery life. Most systems also notify you when the battery is running low, so you can recharge or replace it on time.
Advantages of Battery Power

- Installation Flexibility: You can place these cameras in remote or hard-to-reach areas without worrying about running power cables.
- No Wiring Required: For renters or people who want a cleaner, wire-free look, battery-powered cameras are ideal since they don’t require drilling holes or relying on electrical outlets.
- Portability: Since these cameras are not bound to power sources, they can be easily moved from one place to another.
Challenges with Battery-Powered Cameras
- Frequent Charging or Replacement: Depending on the make and model, you might need to replace or recharge batteries every few months, which can become inconvenient.
- Limited Power Sources: Features like 24/7 recording can drain the battery quickly, requiring more frequent attention.
- Weather Impacts: For outdoor battery-powered cameras, weather fluctuations (such as cold climates) can affect battery performance.
Maximizing Battery Life: Practical Tips
- Use energy-saving features, such as motion detection mode, rather than continuous recording.
- Regularly maintain and clean the camera, as dirt on motion sensors or lenses can cause false triggers and unnecessary power consumption.
- Choose cameras with higher-capacity batteries for fewer recharges.
Who Is Battery Power Best For?
Battery-powered cameras are ideal for homes or businesses where permanent installation may not be practical. They are also great for temporary surveillance needs or remote, off-the-grid locations (such as construction sites).
2. Hardwired Wireless Cameras (Continuous Power)
Though they are called "wireless cameras," not all of them are entirely wire-free. Many wireless cameras are powered by connecting them to standard power outlets or using power-over-ethernet (PoE) connections. These systems rely on a stable and continuous power source while still transmitting video wirelessly via Wi-Fi or other wireless protocols.
How They Work
- Power Outlet Connection: Most hardwired wireless cameras come with a power adapter that you plug into an electrical outlet. The camera continuously draws power to function.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE): In some cases, the camera is connected to a single cable that provides both power and data connection. This setup still counts as "wireless" because no separate power supply is needed apart from the Ethernet cable.
Advantages of Continuous Power
- No Interruptions: You do not have to worry about depleting batteries, so your camera can record 24/7 without interruptions.
- Enhanced Features: Continuous power enables energy-intensive features like night vision, 4K recording, and AI-based motion tracking.
- Lower Maintenance: You won't need to worry about recharging or replacing batteries, reducing upkeep.
Challenges With Continuous Power Cameras
- Wiring Requirements: Though not as demanding as traditional wired systems, these cameras still require proximity to an outlet or a PoE-capable switch/router.
- Limited Placement Options: Since the camera needs to stay near a power source, your installation choices might be fewer compared to battery-powered cameras.
- Power Outages: If your home or business experiences frequent power outages, this might reduce their reliability unless there’s a backup power solution.
Who Are Hardwired Wireless Cameras Suited For?
Hardwired wireless cameras are best for users who want consistent performance without worrying about battery life. They’re a more reliable option for high-security areas requiring continuous recording or special features like cloud storage integration and night vision.
Solar-Powered Wireless Cameras
In addition to battery and hardwired options, some wireless cameras support solar-powered technologies. These cameras typically come with a solar panel accessory, which charges a built-in or replaceable battery. Solar wireless cameras are an excellent solution for areas where traditional power isn’t available, such as rural locations or outdoor spaces.
How They Work
A solar-powered camera captures energy from sunlight during the day. This energy is stored in batteries, allowing the camera to operate even at night or during cloudy conditions. These cameras usually come equipped with energy-efficient protocols to optimize solar usage.
Benefits of Solar Power
- Eco-Friendly: Solar-powered cameras reduce reliance on traditional energy sources and are kinder to the environment.
- Self-Sufficiency: If sunlight availability is consistent, you rarely need to worry about recharging or replacing batteries.
- Versatility: Solar cameras are highly useful in remote areas with no available power outlets.
Drawbacks of Solar Power
- Weather Dependency: Poor weather conditions can disrupt energy storage and affect performance.
- Upfront Cost: Solar-powered cameras and their panels often cost more than standard battery-based systems.
Who Should Choose Solar-Powered Cameras?
These cameras make sense for eco-conscious users or those looking to monitor off-the-grid areas where standard power options are not feasible.
Deciding Between Battery, Hardwired, and Solar-Powered Cameras
When choosing the power source for your wireless camera, consider the following factors:
1. Location: Is the area near an outlet, or does it require flexibility without wires?
2. Environment: Are there weather conditions or natural factors, like sunlight, that may affect performance?
3. Security Needs: Do you need 24/7 monitoring, or is on-demand recording via motion detection sufficient?
4. Maintenance Preferences: Are you comfortable with the effort of charging batteries, or do you prefer a “set it and forget it” approach?
If placement flexibility is important and you don’t mind maintaining batteries, battery-powered cameras are a great choice. For consistent, uninterrupted monitoring in one spot, hardwired cameras are more practical. Lastly, solar-powered options are fantastic when you don't have access to traditional power sources but are located in sunny environments.
Practical Tips When Powering Wireless Cameras
- Backup Power: To ensure uninterrupted security, consider using an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or backup batteries for hardwired wireless cameras.
- Efficiency Features: Many modern wireless cameras come with motion-activated recording or sleep modes to minimize energy usage.
- Optimal Charging Cycles: For battery-powered and solar cameras, avoid overcharging the batteries, as it may impact their longevity.
Wireless cameras are powered through a variety of means, including batteries, continuous power connections, or solar panels. Each option has distinct advantages and limitations, making it essential to assess your needs and environment before making a decision. Battery-powered systems offer unmatched flexibility, hardwired cameras deliver consistent performance, and solar-powered devices combine eco-friendliness with independent operation.
By carefully considering placement, security needs, and maintenance preferences, you can select the best power solution for your wireless cameras and ensure your property stays monitored and secure at all times.




































There are no comments for this blog.